Motivation is a powerful driver of employee performance and organizational success. In this blog, we explore several influential theories of motivation, including Expectancy Theory, Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, Arousal Theory, and Equity Theory, and explain how they can be applied in the workplace. These theories provide practical frameworks to improve employee engagement, foster a culture of fairness, and ensure a productive work environment. By understanding the complex factors that drive motivation, businesses can create tailored strategies to enhance employee satisfaction and long-term success.
Motivation plays a pivotal role in shaping the success of any organization. In the workplace, motivated employees are not only more productive but also more engaged, creative, and committed to their roles. A 2022 study published in Behavioral Sciences found that autonomy and social relatedness positively impact work motivation, while competence has a negative influence. These insights underline the complexity of motivation and its role in employee performance.
Understanding the theories of motivation can help business leaders create an environment where employees feel inspired to perform at their best. In this blog, we’ll explore some of the most influential theories of motivation and how they can be applied to improve workplace motivation and drive long-term success.
What Are Theories of Motivation in the Workplace?
Motivation in the workplace is a driving force that influences employees to contribute their best efforts to their tasks. Various theories of motivation have been proposed over the years, each offering unique insights into the factors that inspire and influence behavior. By applying these theories, companies can tailor their approach to maximize employee engagement, satisfaction, and productivity.
The right understanding of motivation in the workplace can lead to enhanced performance, greater job satisfaction, and reduced turnover. Let’s dive into some key theories that can help organizations unlock their employees’ true potential.
Expectancy Theory of Motivation: Why Effort and Rewards Matter in the Workplace
One of the most widely applied theories of motivation in workplace settings is expectancy theory of motivation. This theory, developed by Victor Vroom, suggests that employees will be motivated to work harder if they believe their efforts will lead to successful performance, and ultimately, to desired rewards.
Core Elements of Expectancy Theory
The expectancy theory highlights three critical components that influence workplace motivation:
Expectancy (Effort → Performance): Employees need to believe that their effort will lead to higher performance. If they think working hard won’t make a difference, they are less likely to put in the effort.
Instrumentality (Performance → Outcome): This component centers on the belief that good performance will be rewarded. If employees perceive that high performance is recognized and rewarded, they are more likely to stay motivated.
Valence (Value of Rewards): Employees must value the rewards that come with high performance. This could be a salary increase, promotion, recognition, or even personal fulfillment. If the rewards aren’t meaningful, employees will lose motivation.

Applying Expectancy Theory to Improve Workplace Motivation
Employers can use the expectancy theory of motivation to design incentive programs that align with the expectations and desires of their workforce. For example, clear career advancement paths and transparent reward systems help reinforce the connection between effort, performance, and rewards.
By understanding what motivates individual employees, businesses can create a more motivating and performance-driven work environment. A good performance management system should align employee goals with the company’s objectives, ensuring that both personal and organizational growth are achieved simultaneously.
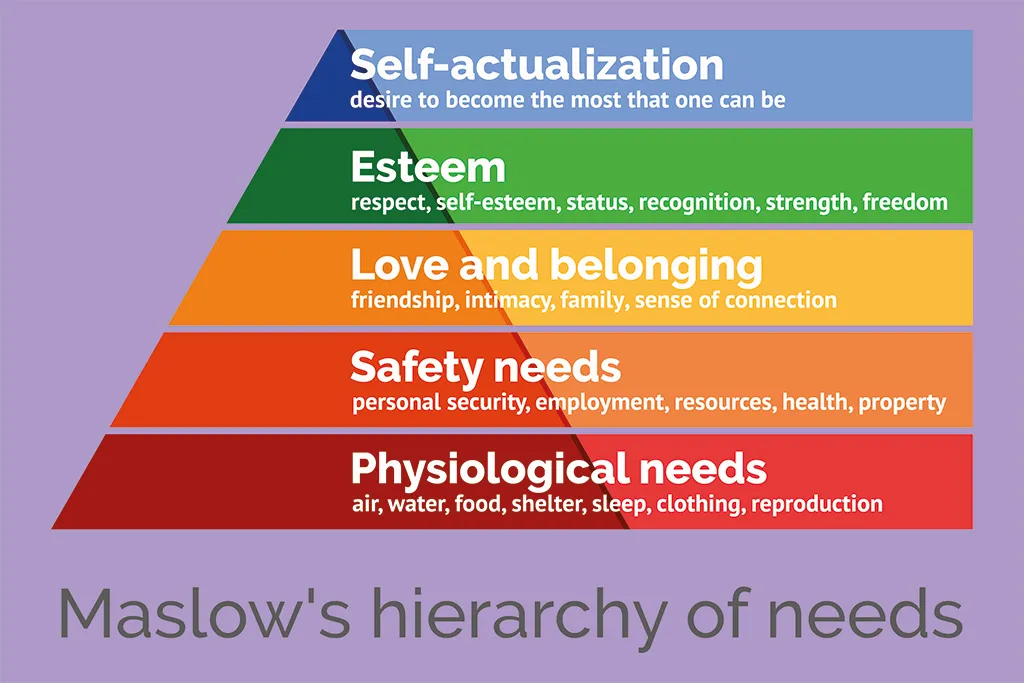
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs: Motivating Employees Beyond Basic Needs
Maslow’s theory of motivation is one of the foundational theories that can transform the way we approach employee motivation in the workplace. Maslow proposed a hierarchy of needs that suggests human beings must satisfy their lower-level needs before they can be motivated by higher-level ones.
(source:https://www.peoplemanagement.co.uk/article/1796563/why-need-go-beyond-maslow)
The Five Levels of Maslow’s Hierarchy in the Workplace
Maslow’s hierarchy has five levels, each building upon the previous one:
Physiological Needs: Basic needs like food, water, and rest. In the workplace, this could translate to ensuring that employees receive fair wages, have access to breaks, and work in comfortable conditions.
Safety Needs: The need for security and stability. In a work context, this might involve job security, health benefits, and safe working environments.
Social Needs: Employees need to feel a sense of belonging and community. Fostering a positive workplace culture, where employees feel valued and connected, helps fulfill this need.
Esteem Needs: Recognition and respect are key to employee motivation. Providing opportunities for employees to achieve and be recognized for their accomplishments can satisfy their esteem needs.
Self-Actualization: The highest level of Maslow’s pyramid is self-actualization, which involves personal growth and achieving one’s potential. In the workplace, offering opportunities for professional development and skill-building can help employees reach this level of motivation.
Using Maslow’s Theory to Motivate Employees at All Levels
Understanding Maslow’s hierarchy allows companies to address different motivation needs based on where employees are on the pyramid. For example, employees who are struggling to make ends meet may prioritize wages (physiological needs) over professional development. Meanwhile, high performers may be more motivated by opportunities to advance their careers (esteem and self-actualization).
By addressing the full spectrum of employee needs, organizations can foster a more satisfied, productive, and motivated workforce.
Arousal Theory of Motivation: Finding the Right Stimulus for Employee Engagement
The arousal theory of motivation suggests that people are motivated to maintain an optimal level of arousal. This means employees are driven by the need for stimulation or excitement, and they seek activities that either increase or decrease their arousal to maintain a comfortable balance.
Understanding Arousal in the Workplace
Every individual has a unique optimal arousal level. Too little arousal can lead to boredom and disengagement, while too much can cause anxiety or burnout. In the workplace, motivation is often linked to finding the right level of stimulation.
For example, monotonous or repetitive tasks might lead to decreased motivation, while employees facing tasks that are too challenging or stressful might experience burnout. The key is to provide employees with tasks that are appropriately challenging, allowing them to engage with their work without feeling overwhelmed.
How to Apply Arousal Theory to Foster Engagement
To apply the arousal theory in the workplace, it’s important to find ways to balance routine tasks with opportunities for new challenges. Rotating tasks, offering skill development programs, or creating a competitive yet supportive environment can help maintain motivation levels.
Incorporating variety into employees' daily routines, such as offering collaborative projects, new learning opportunities, and job rotations, can also increase engagement and performance.
Equity Theory of Motivation: Promoting Fairness and Justice in the Workplace
Equity theory of motivation developed by John Stacey Adams, focuses on fairness and justice in the workplace. According to this theory, employees are motivated when they perceive fairness in the distribution of rewards. If employees believe they are treated equitably in comparison to their peers, they are more likely to feel motivated and committed to their work.
How Equity Theory Works in the Workplace
Equity theory is based on the idea that employees compare their inputs (effort, skill, time) and outputs (salary, recognition, benefits) to those of others. If they perceive an imbalance, motivation can suffer.
Equity: When employees feel they are fairly compensated for their efforts, they are more likely to stay motivated and productive.
Inequity: When employees perceive inequity—whether being under-rewarded or over-rewarded—motivation can decrease, leading to dissatisfaction, disengagement, or even turnover.
Using Equity Theory to Improve Workplace Motivation
Managers can use the equity theory of motivation to ensure that compensation, recognition, and workload are distributed fairly among employees. Regular performance evaluations and transparent communication regarding promotions and pay raises can help reinforce a sense of fairness.
Creating a transparent, equitable workplace culture that values each employee’s contribution is critical for maintaining motivation and morale.
How These Motivation Theories Impact Your Workplace
Understanding and applying the theories of motivation can be a game-changer for workplace dynamics. Whether you're an employee seeking to enhance your performance or a leader striving to improve team morale and productivity, these theories offer practical insights for achieving your goals.
For example, fostering a work environment that recognizes Maslow’s hierarchy of needs helps ensure that all employees’ basic needs are met, which can increase satisfaction and loyalty. Similarly, applying expectancy theory can motivate employees by aligning their effort with rewards. Tools like the Nearity C50 can further enhance motivation by providing an environment where communication flows seamlessly, and employees feel empowered to perform at their best.
As a leader, regularly evaluating how well you are meeting your employees’ motivational needs can help you develop more targeted strategies for increasing engagement, productivity, and retention.
Conclusion: The Key to Motivated, High-Performing Employees
Theories of motivation are not just academic concepts—they are essential tools for shaping workplace culture and driving employee performance. Whether through the framework of expectancy theory, Maslow’s hierarchy, or equity theory, understanding what motivates employees helps organizations foster a more positive, productive environment.
Incorporating these motivation theories into your leadership strategies can lead to more engaged employees, higher performance, and greater satisfaction. By investing in employee motivation, companies can unlock their full potential, resulting in success for both the individual and the organization.
If you're looking for more ways to enhance your workplace performance, consider tools that can optimize communication and collaboration. Our All-in-One Meeting Camera C50 is designed to elevate your virtual meetings and improve teamwork in any workspace. Whether you're working remotely or in the office, the C50 Camera ensures seamless communication and boosts productivity, helping your team stay connected and motivated.
Motivation is the key to unlocking potential—both for your employees and your business. Start applying these theories today to create a more motivated and high-performing workplace!
FAQs About Workplace Motivation Theories
What is the most effective motivation theory for improving workplace performance?
The most effective motivation theory depends on your workplace needs and employee preferences. The expectancy theory is particularly useful when aligning employee effort with rewards. However, for employees seeking personal growth, Maslow's hierarchy of needs can be more applicable, as it addresses different levels of motivation.
How do I know if my employees are motivated?
You can measure motivation through employee engagement surveys, one-on-one meetings, and productivity metrics. If employees feel they are not receiving sufficient recognition or rewards, they may become disengaged.
How can I use Maslow’s hierarchy to motivate my employees?
Start by ensuring employees' basic needs are met (e.g., fair pay, safe working conditions). Then, focus on fostering social connections through team-building activities. Recognition and career development opportunities are essential for meeting esteem and self-actualization needs.
Can motivation theories apply to remote teams?
Absolutely! Motivation theories are universal and can be applied to both in-office and remote employees. Tools like the All-in-One Meeting Camera C50 can help remote teams stay connected, engage in productive meetings, and feel valued—helping to maintain motivation levels even from a distance.








































































